Supply Chain VC Update; What’s Next for U.S.-Mexico Trade; Regulations Roundup; and more Logistics News
A look at the latest news stories in global supply chain and logistics.
Supply Chain VC Update
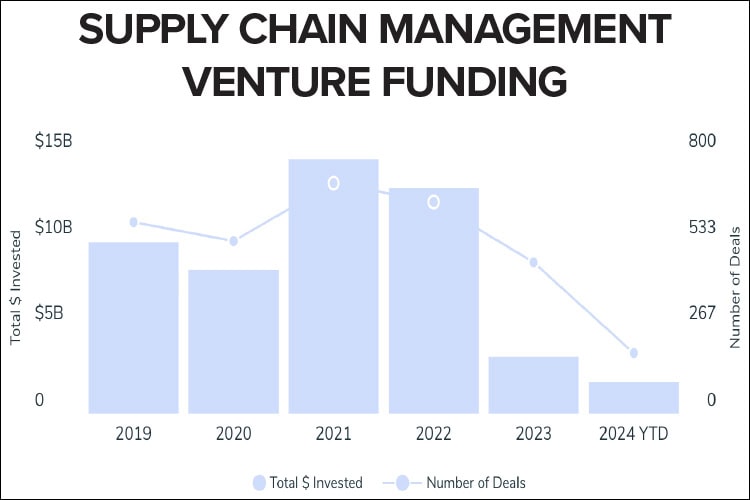
Could the relative calm in supply chains in 2023 and 2024 versus the major disruptions in 2021 and 2022 be dampening investor enthusiasm for supply chain-related deals? A Crunchbase analysis indicates as much.
Crunchbase data shows total venture funding to supply chain startups has yet to hit $2 billion this year—a pace that, if continued, will result in a 79% drop from the all-time high set in 2021 of $14.7 billion. At its current rate, the total is likely to fall short of the $3.3 billion raised in 2023.
There are a few exceptions. Logistics giant Flexport—which less than 3 years ago hit a peak valuation of $8 billion—raised $260 million from partner Shopify in January. And Altana AI, a company that “empowers governments, logistics providers, and enterprises with an intelligent, dynamic map of the global supply chain” nabbed $200 million in Series C funding in July.
Otherwise, deal flow in the supply chain sector has declined dramatically, with Crunchbase predicting only slightly more than 300 deals will close this year—a 55% drop from 2021’s 711 and a decrease of more than nearly 150 rounds from last year.
Crunchbase notes that venture funding has been down in nearly every sector since 2021, but the decrease in supply chain-related funding has been especially sharp.
Survey Says: It’s Risk Management Over Cost
A shift is afoot when it comes to selecting and locating global supply chain networks. Instead of focusing solely on lowest-cost strategies, leaders are emphasizing building resilience, agility, and flexibility into their supply chains, shows new research from Gartner.
The data shows that these risk management considerations have displaced cost-efficiency as the top drivers of network changes. Here are some key takeaways from the global survey:
- 73% of companies have added or removed production locations from their supply chain networks in the past two years.
- Of those that have made changes in the past two years, 90% report that they have met or exceeded the expected benefits of the change.
- Despite the early success of these network shifts, 96% of respondents cite challenges with operating in new locations; operational and logistics costs are cited most often.
- A shortage of factory workers was a more common challenge in North America compared to all other regions.
Supply Chain Sustainability Trends
 Q&A with Jeff Pepperworth, President & CEO, iGPS Logistics
Q&A with Jeff Pepperworth, President & CEO, iGPS Logistics
Sustainability has been an industry buzzword for a while now. What are some new/current trends you are seeing?
Even though sustainability is not a new initiative, we see the adoption of greener supply chain practices on a much larger scale. Previously, bigger-name brands were the main players advocating for the implementation of more eco-friendly practices. But because big retailers have been pushing their suppliers to adopt sustainability programs, we now see a ripple effect, and more secondary and tertiary players are putting environmental responsibility at the forefront.
Are there any buzzy sustainability efforts companies should be more aware of, such as new developments with AI and other tech?
While route-planning technology has been around for a while, it is certainly becoming more advanced, and we have more electronic “eyes” on our roadways than ever to help shippers identify ways to optimize. AI is also creating dimensional references to build packaging that is specific to items being shipped—cutting down on dunnage and wasted space—and ensuring that boxes on pallets are cubed more efficiently, so more products can be transported at once. This all adds up to reduced greenhouse gas emissions in the atmosphere.
The market for green bonds and other sustainability bonds hit a growth milestone last year. What can you tell us about these bonds and what they mean for supply chain and environmental sustainability?
When you look at the investment marketplace, it’s clear that investors— including institutional investors, angel investors, and VC firms—are increasingly looking to include sustainable investment vehicles as part of their portfolios. Not all consumers are investors, but all investors are consumers. They are looking to invest in sustainable brands in the same way that consumers are looking to do business with sustainable brands. Here at iGPS, we have multiple participants in our own green bonds, and we expect that the pallet industry will continue to move in this direction.
How can the supply chain sector as a whole help to get sustainability moving forward in a stronger direction?
It comes down to unification. In what ways can we unify the supply chain sector around common sustainability goals? For example, many years ago the grocery industry standardized the pallet. It was recognized that a consistent asset of specific dimensions was necessary to ensure that all forklifts and warehouse racking could handle pallets.
So, what else can we unify? Can we make water packaging or egg cartons consistent so that these products have the same density and can be transported more efficiently, without impacting the spirit of competition? If we look at the supply chain holistically and discover new ways to adopt common standards, we can move toward an even greener and healthier future.
Freight & Capacity Forecast
With less than half of 2024 remaining, supply chain professionals are looking back at what has already transpired—and what issues are left to contend with before the year draws to a close. Thus far, the supply chain has faced several significant challenges with lasting global implications, including the effects of ongoing geopolitical tensions and the threat of labor strikes in the United States, Canada, and Europe.
According to FTI Consulting’s Q2 2024 Transportation & Logistics Industry Update, the transportation and logistics market saw a surge in ocean freight prices and growing demand for air freight due to longer transit times caused by Red Sea shipping disruptions and congestion in Asian ports. However, an increase in capacity and the opening of new sea routes are expected to reduce freight prices in 2025 despite current T&L pricing pressures.
Here’s a roundup of the report’s findings from Q2 2024 and some upcoming predictions:
Global Freight Market Outlook
The global freight market shows steady growth in volume, reflected by an increase in the number of M&A deals and rising demand for air freight forwarding services.
 – Increased volumes coupled with disruptions in major shipping routes have led to significant increases in demand for air and ocean freight in 2Q24.
– Increased volumes coupled with disruptions in major shipping routes have led to significant increases in demand for air and ocean freight in 2Q24.– Hostile developments in the Red Sea have presented manifold challenges for global trade, ranging from extended transit durations and capacity limitations to elevated expenses and increased uncertainty.
 – General cargo has shown faster growth than specialized products in 2024, due to increasing demand from ecommerce and disruptions in the container shipping sector.
– General cargo has shown faster growth than specialized products in 2024, due to increasing demand from ecommerce and disruptions in the container shipping sector.– Air cargo is set for a strong second half, driven by sustained ecommerce growth, increasing ocean shipping costs, and disruptions in the Red Sea.
 – Entering 2024, shippers expected a buyer’s market for ocean freight, with carriers adding capacity in 2023 and planning to do so again. Instead, global geopolitical events and high demand across trade lanes in 2Q24 have reduced available capacity and increased shipping rates.
– Entering 2024, shippers expected a buyer’s market for ocean freight, with carriers adding capacity in 2023 and planning to do so again. Instead, global geopolitical events and high demand across trade lanes in 2Q24 have reduced available capacity and increased shipping rates.– Due to the necessity of rerouting via the Cape of Good Hope, new capacity added in 2023 and early 2024 hasn’t been sufficient to meet growing demand.
Source: FTI Consulting
IRA/CHIPS Logistics Projects Stalled

The bipartisan Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and CHIPS and Science Act, both passed in 2022, generated buzz in the supply chain sector for a predicted resurgence of manufacturing activity that would yield increased demand for logistics services and investments. However, two years later, some enthusiasm is waning as nearly half of the manufacturing projects envisioned under IRA and CHIPS have stalled, according to a Financial Times investigation. The slowdown has created uncertainty around the demand for logistics space.
Forty percent of the largest U.S. manufacturing investments announced during the first year of President Biden’s industrial and climate policies have been delayed or paused, the Times found. A total of $84 billion of those projects have been delayed for at least two months and some have been paused indefinitely. Deteriorating market conditions, slowing demand, and lack of policy certainty were cited as reasons for the delays.
Across the nation, large projects on hold include Enel’s $1 billion solar panel factory in Oklahoma, LG Energy Solution’s $2.3 billion battery storage facility in Arizona, and a $1.3 billion lithium-ion refinery in South Carolina, according to the report.
The tax credits and grants stretch into 2032, but inflation, labor shortages, and supply chain challenges are all contributing to delays in achieving project milestones, which are key to unlocking funding.
All Eyes on Mexico

Cross-border commerce and nearshoring have been a growing focus for many global shippers over the past few years—and events resulting from Mexico’s historic election in June 2024 seem to indicate that trend will continue.
That’s the consensus from Redwood Mexico’s Q3 Cross-Border Index. The election, which saw the country choose its first female president amid unprecedented levels of violence, has led to notable shifts that impact the U.S.-Mexico trade landscape, including the peso’s devaluation, shifting market dynamics, and an increased call for security.
The report highlights these shifting trends:
- Currency complexity: The peso’s devaluation has provided relief for Mexican truckers and boosted export competitiveness, but also introduces new challenges for foreign direct investment.
- Trade dominance: The competitiveness of Mexican commerce is on display as trade volumes through Laredo, Texas have been consistently rising, surpassing traditionally dominant international ports. For 15 of the past 16 months, Laredo has seen higher throughput than the Port of LA/Long Beach, which once processed nearly 50% of all foreign imports.
- Labor: Spurred by rising labor costs in Asia and ongoing trade disputes, Mexico continues to grow as a manufacturing and commerce hub, both with the United States and globally. Imports from Asia into Mexico have risen, pointing to the growth in Mexican ports as a way to work around U.S. tariffs on Asian goods.
- Safety: The new administration under President-elect Claudia Sheinbaum vows to improve security on Mexican highways, responding to long-standing concerns. This includes increased law enforcement presence, which should have positive impacts on future trade volumes and safety.
Are You Up to Speed with the Latest Regulations?
The U.S. supply chain, transportation, and logistics sector is continuously evolving, influenced by new technologies, global trade dynamics, and changing consumer expectations. To keep pace, U.S. government agencies regularly update and introduce regulations that impact how businesses operate in these critical areas.
Here is an overview of some of the most significant new and updated regs shippers need to stay abreast of.
Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA)

FMCSA, the key agency responsible for regulating commercial motor vehicle safety in the United States, announced four recent updates to address the evolving needs of the trucking industry.
1. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) Systems Rule: Last year, FMCSA, in collaboration with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), proposed a rule that would require automatic emergency braking systems in U.S. light vehicles and trucks. The rule was finalized in May 2024 and goes into effect in September 2029.
2. Expansion of Drug and Alcohol Clearinghouse Requirements: As of 2023, all state driver licensing agencies are required to use the Clearinghouse to check whether a driver is prohibited from operating a commercial motor vehicle due to drug or alcohol violations before issuing, renewing, or upgrading a commercial driver’s license.
3. Electronic CDL Information Exchange: As of August 2024, states are required to implement an all-electronic system for exchanging commercial driver’s license (CDL) information, including convictions and disqualifications, to streamline and improve the accuracy of CDL record-keeping.
4. Hour of Service (HOS) Updates for Agricultural and Livestock Haulers: FMCSA updated the HOS regulations in 2023 specifically for agricultural and livestock haulers to provide more flexibility for haulers during planting and harvesting seasons while maintaining safety standards.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)

The EPA has introduced several new regulations aimed at reducing environmental impacts associated with transportation and logistics, particularly concerning emissions and sustainability. Here are two important developments:
1. Heavy-Duty Engine and Vehicle Standards: The EPA recently finalized new emissions standards for heavy-duty vehicles and engines, starting with model year 2027. These standards are designed to significantly reduce nitrogen oxide emissions, which contribute to smog and respiratory issues. The rules also set stricter greenhouse gas emission standards for medium and heavy-duty trucks, promoting the adoption of cleaner technologies.
2. Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) Rule: Several states, including California, adopted the ACT rule, which required manufacturers to sell an increasing percentage of zero-emission trucks annually, starting in 2024. The EPA is expected to introduce similar nationwide regulations to support the transition to electric and hydrogen-powered trucks.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
The FDA continues to update its regulations to ensure the safety and security of the food and pharmaceutical supply chains. Recent changes include the following:
1. Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Final Rule on Food Traceability: In response to ongoing concerns about foodborne illnesses, the FDA issued the final rule on food traceability in 2023. The rule establishes additional recordkeeping requirements for certain foods, facilitating faster identification and removal of potentially contaminated products from the market.
2. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA): The FDA has ramped up enforcement of the DSCSA, which aims to enhance the security of the pharmaceutical supply chain. Starting this year, all prescription drugs in the United States are now required to be traceable at the package level throughout the supply chain. This will help prevent counterfeit drugs and improve the ability to respond to recalls and quality issues.
Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
CBP continues to play a crucial role in regulating international trade, with recent updates aimed at elevating security and efficiency in global supply chains.
1. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act Expansion: The UFLPA focuses on preventing goods produced with forced labor in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR) of China from entering the U.S. market. Earlier this year, CBP intensified its enforcement efforts under UFLPA, expanding the UFLPA Entity List, which identifies entities involved in forced labor practices in XUAR, by adding 26 new entities believed to be sourcing materials from the region.
2. Modernization of the Automated Commercial Environment (ACE): CBP has made significant updates to the ACE system, which facilitates electronic processing of imports and exports. The updates include enhanced functionality for managing trade compliance and security, such as better tools for filing and processing entries, and new features for monitoring trade trends and risks.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)

OSHA has launched new initiatives focusing on safety in warehouses and distribution centers. These include increased inspections and enforcement related to hazards such as ergonomic injuries, forklift safety, and heat exposure, reflecting the growing importance of warehousing in the e-commerce-driven supply chain. The agency has also updated training requirements and enforcement strategies to reduce fall-related injuries and fatalities.

